Hands on Elasticsearch.
Elasticsearch is a document-oriented search engine based on Lucene library. The use case I have in my work is about searching relevant documents in large document database systems based on specified keywords, where Elasticsearch can be perfectly applied. As it has open source version, I decide to build a blog search engine for my past posts at this site.
1. Download and Configure Elasticsearch
First download elasticsearch-7.7.1 from elastic. Next go to /elasticsearch-7.7.1/config/elasticsearch.yml, I only change network.host to "localhost", other fields remain defaults. Then run command in /elasticsearch-7.7.1/bin/
|
|
Then go to http://localhost:9200/, see
|
|
indicates elasticsearch engine is already on.
2. Kibana Dashboard
There is a dashboard called kibana can be used to visualize data. Download kibana and go to /kibana-7.7.1/bin run
|
|
Then the dashboard will be run at http://localhost:5601/.
3. Import Data
The posts I have are all in markdown files, I use python to process and save all of them into a single csv file (see notebook). The csv file can be imported into kibana.
A screenshot of the dashboard
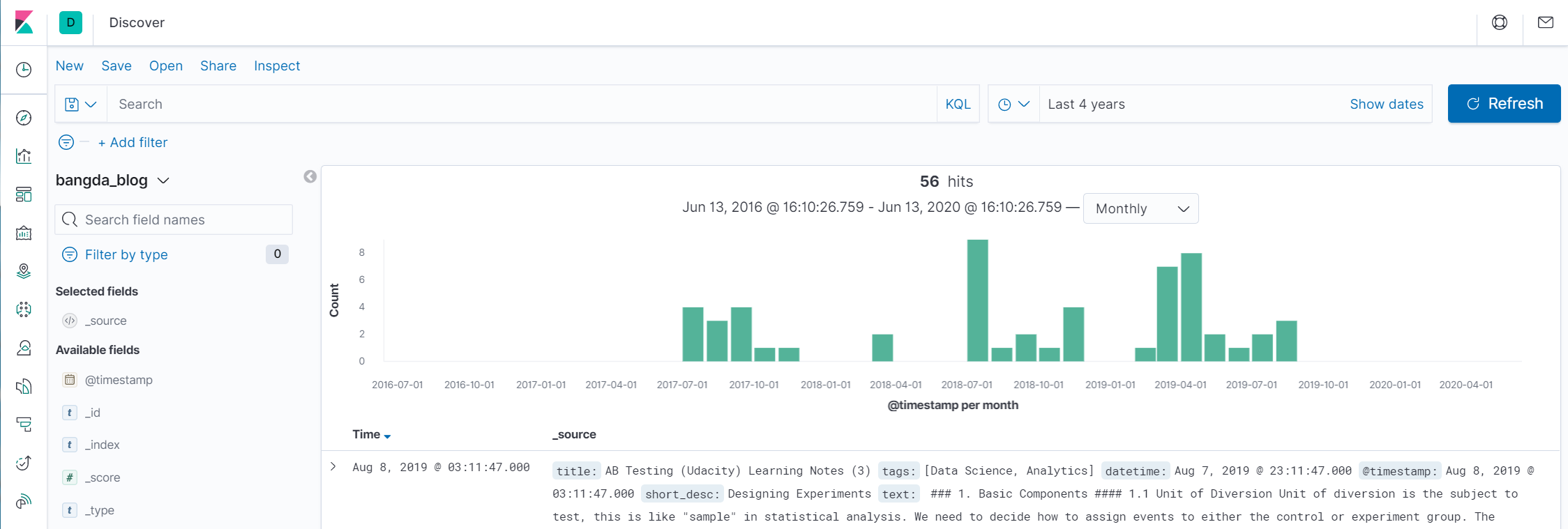
As the dashboard shows, I have 56 blogs until now. There are several periods that I have high productivity: 2018/07, 2019/03 and 2019/04.
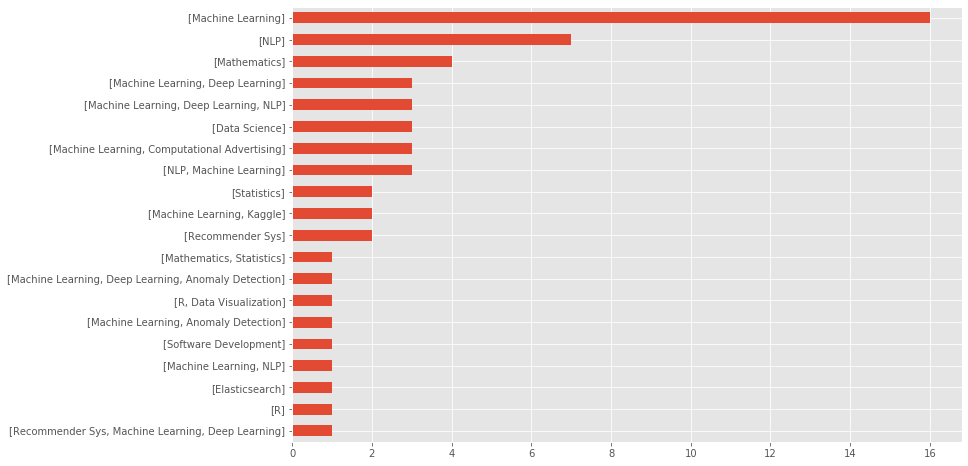
And the distribution of blog category is like this
4. Query Blogs
In the query window, run
|
|
All blogs with “recommender” in the title will be returned:
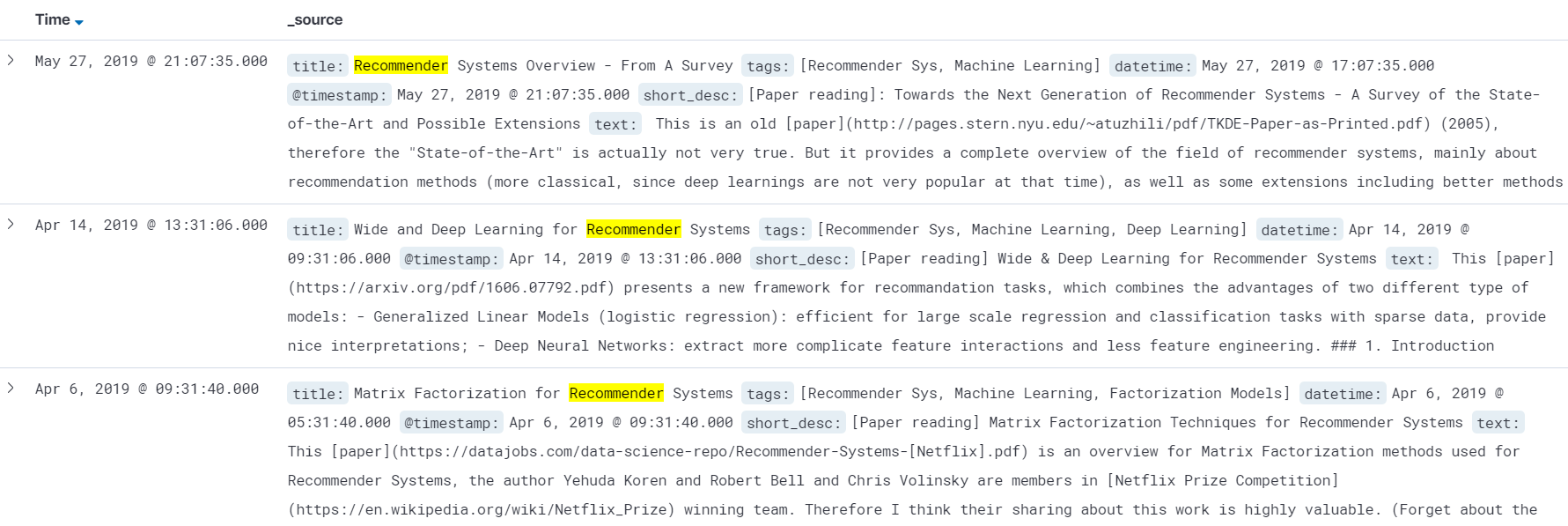
A more extensive exploration of query can be found in this notebook.
5. Visualization Using Wordcloud
Using elasticsearch_dsl can query data using python. First check all blogs with title contains “recommender”:
|
|
Three blogs are returned, the score here is by default using Lucene’s Practical Scoring Function. This is a similarity model based of Tfidf for queries.
|
|
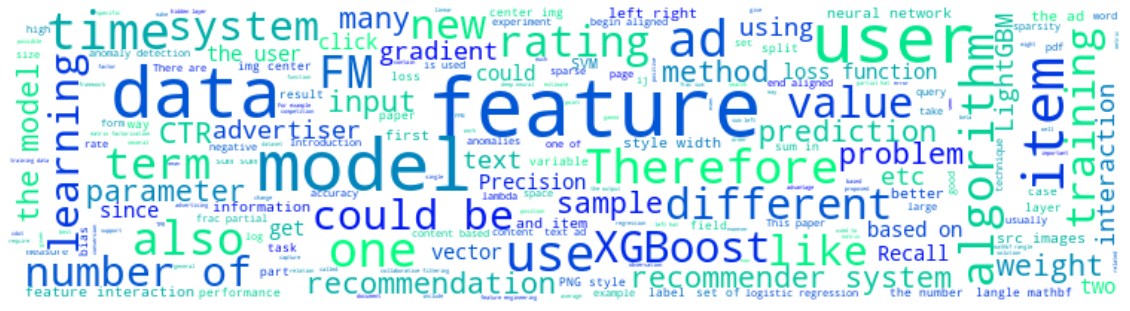
A wordcloud of these three blogs:

Another wordcloud for blogs contains “machine learning” in tags.
Here is the notebook used to query blogs and generate wordclouds.